Glossary
The following are terms to know in alphabetical order (not in an order that you should learn these concepts)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
A division of the nervous system that is comprised of the Brain and Spinal Cord.
CerebroSpinal Fluid (CSF)
A Fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord. It acts as a shock absorber and caries nutrients to nervous system cells and waste away from them. It is renewed by the body by volume about 4-5 times a day. It is separated from other bodily fluids by the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).
Glial Cells
Milieu
Another term for "Environment", as in cellular environment / cellular Milieu
Neuron
The basic nervous system cell responsible for receiving, processing, and outputting signals due to being electrically and chemically excitable and due to their asymmetric makeup.
Neurons are not the primary type of cell of the nervous system, they are outnumbered by Glial cells three to one!
(Principles of Neural Science - McGraw Hill (2021): Part 1 - Chapter 3)
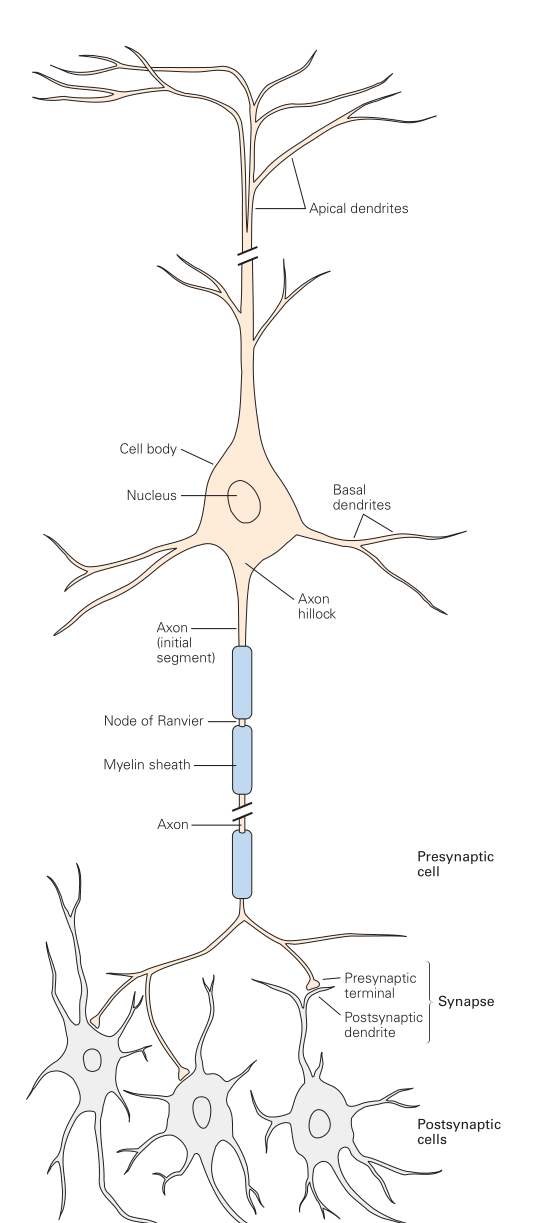
The basic structure of a neuron consists of:
- Dendrites: Branches coming off the center cell body, are generally small but numerous, and act as the input for the neuron
- Cell body / Cell Soma: The 'Center' of the neuron, which is where the nucleus is contained
- Axon Hillock: The protrusion of the soma before it becomes the axon, where all input signals from the dendrites are combined where they may reach the firing threshold and trigger an action potential
- Axon: The output of the neuron, where action potentials flow out to other enervated neurons or receptor cells
There are hundreds of neuron types and they can be categorized in various manners:
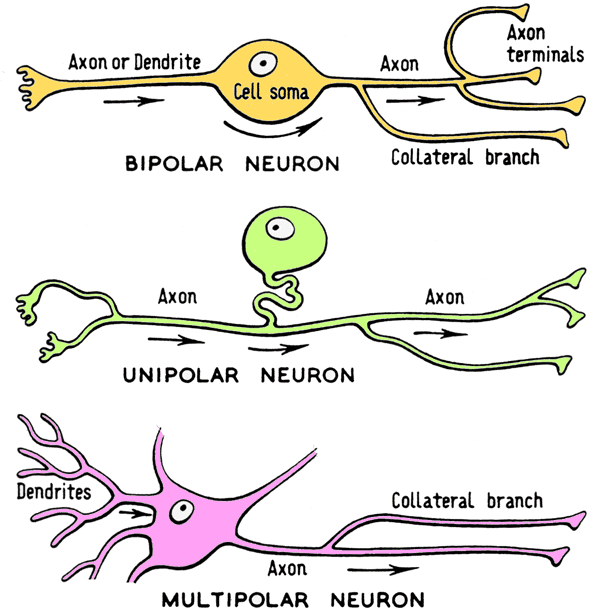
Polarity
Neurons can be structured in slightly various manners to better fit their specific role. They can be Bipolar, Unipolar, or Multipolar.
Afferent / Interneuron / Efferent
Names of categories referring to the general functional role of a neuron.
- Sensory / Afferent: Receives data from the outside world.
- Tend to be unipolar or bipolar.
- Example: Photo-receptor.
- Interneuron: Neurons that connect to other neurons. Does not receive input from the world, nor directly control any response. Are typically involved in information processing.
- Tend to be multipolar.
- Example: Most of the neurons in the brain.
- Motor / Efferent: Outputs a response to the outside world. Typically to a muscle but potentially also to things like glands.
- Tend to be multipolar.
- Cell body is often found in the spine
- Example: Nerve innervating a muscle
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
A division of the nervous system, composed of nerves that branch out from the CNS (like out of the spinal cord). Basically anything part of the nervous system that isn't the Brain or Spinal Cord themselves.